PUBLICATIONS
Main Content


Lightweight Security Hardware Architecture Using DWT and AES Algorithms
ABSTRACT: The great increase of the digital communications, where the technological society depends on applications, devices and networks, the security problems motivate different researches for providing algorithms and systems resistant to attacks, and these lasts need of services of confidentiality, authentication, integrity, etc. This paper proposes the hardware implementation of an steganographic/cryptographic algorithm, which is based on the DWT (Discrete Wavelet Transform) and the AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) cipher algorithm in CBC mode. The proposed scheme takes advantage of a double-security ciphertext, which makes difficult to identify and decipher it. The hardware architecture reports a high efficiency (182.2 bps/slice and 85.2 bps/LUT) and low hardware resources consumption (867 slices and 1853 LUTs), where several parallel implementations can improve the throughout (0.162 Mbps) for processing large amounts of data.

Reconfigurable arithmetic logic unit designed with threshold logic gates
ABSTRACT: In recent years, there is a trend towards the development of reconfigurable circuits where devices using them offer flexibility and performance. Different technologies are explored, such as threshold logic gates (TLGs), which are one of the most promising future technologies, and researchers are examining and improving different characteristics such as density, performance and power dissipation. This research presents a 4-bit arithmetic logic unit (ALU), which was designed using TLGs through reconfigurable logic blocks with a universal circuit configured with three stages based on a floating-gate metal oxide semiconductor transistor with more than one control gate, which was named neu-complementary metal oxide semiconductor (ν-CMOS). The main contribution is that this device is configured as a ν-CMOS inverter and has the ability to program the threshold voltage of its transfer curve by applying an external voltage to the additional control gates. The number of input bits and the magnitude of the weighted input capacitances related to control gates of the ν-CMOS inverters is obtained and analyzed by using the graphical method (floating-gate potential diagram). Finally, the proposed 4-bit ALU shows similar results as those measured from the ALUs implemented in the field programmable gate array evaluation kit and the Motorola chip MC14581B.

Blind Tamper Detection to Copy Move Image Forgery using SURF and MSER
ABSTRACT: The sharing of digital images has become a common practice in our daily life, with the risk that these images can be accessed and easily modified by malicious people with the intention of causing moral or economic damage; or even to incriminate innocent people in legal issues. This paper proposes an algorithm to authenticate digital images by means of blind tampering detection against one of the principal manipulations that an image is put through, i.e. the Copy-Move which intends to erase or replicate a part of the image. The development and evaluation results of this proposal are presented in this paper.

Blind Detection for Image Forgery using Blur Edge Detection
ABSTRACT: This paper proposes a blind authentication method for images tampered by copy-paste. Proposed algorithm is based on the blurred edge detection method which is a common technique on photomontages. In the proposed method firstly the image under analysis is filtered to emphasize the edges. Next the natural logarithm is computed to decompose the image under analysis in the sum of luminance and reflectance components. These components are then transformed to frequency domain using the fast Fourier transform. Next using a homomorphic filter, the high frequencies of the image under analysis, where the blur edges are located, are accentuated. Finally the image is transformed to the spatial domain and using a Laplacian Gaussian operator the edges are found. Evaluation results show the forgery detection capability of proposed method.

Image authentication using perceptual hashing
This paper presents a review of image authentication methods, based on the perceptual image hashing approach. Firstly we analyze two algorithms, which have the capability of determining if an image is authentic or not, even if it has suffered content preserving distortions such as compression, filtering and other signal processing operations; as well as some malicious modification such as geometric distortions. Next two modifications of these algorithms are analyzed which improve their performance by increasing their robustness against geometric distortions providing them also tamper detection capability. Finally two recently proposed algorithms with not only the tamper detection capability, but also with the capability of localizing tampered regions are described. Evaluation results are given to show the performance of these methods under analysis.
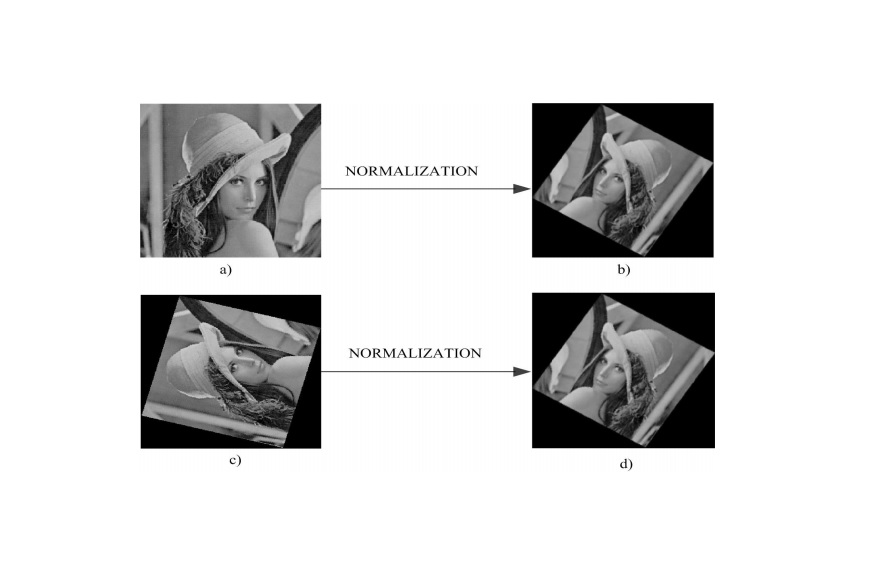
Improvement of Radon Transform-based Perceptual Hashing using Image Normalization
Image Hashing has several applications such as image authentication, image indexing and broadcast monitoring. In the content authentication applications, the hash values of perceptually similar images generated by content preserving modification, such as compression and moderate geometric distortions, also must be similar. Taking this into account we propose an improvement of the Radon transformbased image hashing algorithms, introducing an image normalization algorithm in the preprocessing stage. In the proposed scheme, robustness against geometrical distortions is increased considerably, while keeping the robustness to other content preserving modifications, such as compression, and filtering, which are offered by Radon transform.
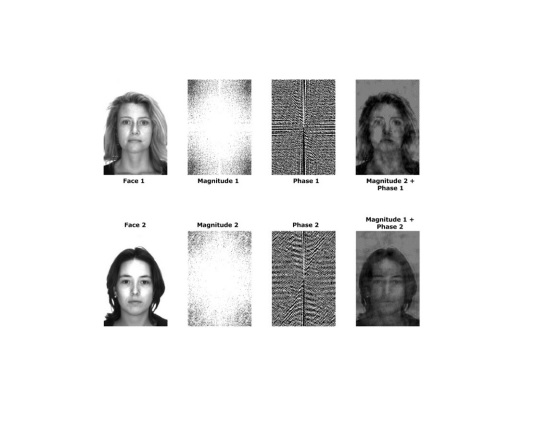
A Face Recognition Algorithm using Eigenphases and Histogram Equalization
ABSTRACT: This paper proposes a face recognition and verification algorithm based on histogram equalization to standardize the faces illumination reducing in such way the variations for further features extraction; using the image phase spectrum and principal components analysis, which allow the reduction of the data dimension without much information loss. Evaluation results show the desirable features of proposal scheme reaching recognition rate over 97% and a verification error lower than 0.003%.
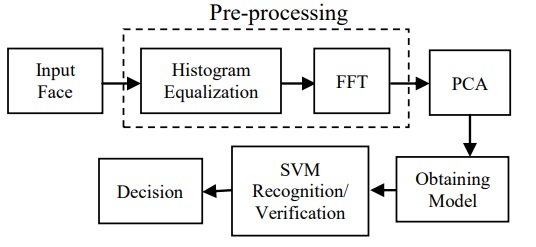
Face recognition and verification using histogram equalization
ABSTRACT: This paper proposes a face recognition and verification algorithm based on histogram equalization to standardize the faces illumination reducing in such way the variations for further features extraction; using the image phase spectrum and principal components analysis, which allow the reduction of the data dimension without much information loss. Evaluation results show the desirable features of proposal scheme reaching recognition rate over 97% and a verification error lower than 0.003%.